For gamers, digital artists, and multitasking computer users, the Graphics Processing Unit is a critical component. Yet, there’s nothing more frustrating than encountering GPU artifacting—an anomaly on the screen that disrupts your visual experience.
While ensuring your GPU functions optimally is crucial, enhancing your gaming device’s storage can also significantly boost performance, as seen with the potential benefits of a Steam Deck SSD upgrade.
The Root of the Problem
When your screen starts showing unexpected visuals or glitches, it could be a result of graphic card artifacting. But what causes these anomalies?
What is GPU Artifacting?
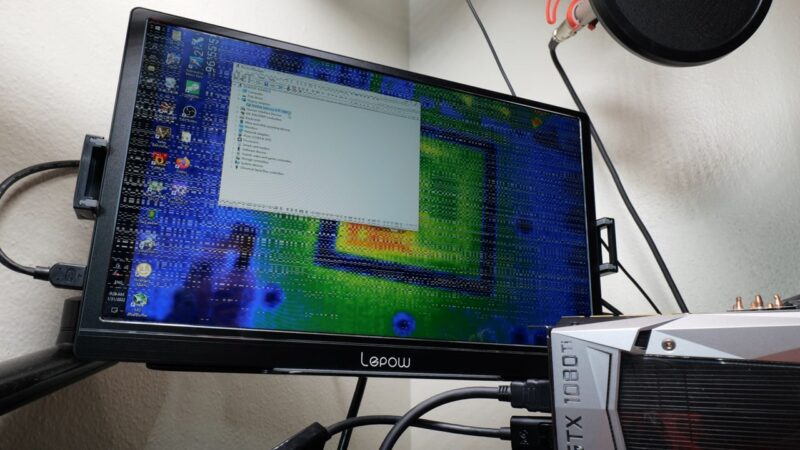
GPU artifacting manifests as strange, often colorful patterns, lines, or blocky areas on your screen. These unwanted visual distortions are a result of the GPU not rendering the graphics correctly.
While transient artifacts might be harmless, persistent ones can hinder your computing or gaming experience and may suggest underlying hardware or software issues.
Common Causes of Artifacting
Identifying the root cause of artifacting can be instrumental in its resolution. Overheating is a primary culprit, where the graphic card gets too hot and starts malfunctioning.
Other causes include factory overclocking, driver issues, insufficient power, or the GPU nearing the end of its lifespan.
Diagnosing the Issue
Before diving into potential solutions, it’s crucial to diagnose the problem correctly. This will ensure you apply the most appropriate fix.
Testing with Different Applications
See if the artifacting is consistent across various applications. Running multiple applications, especially graphic-intensive ones, can help determine if the issue is with a specific software or more generalized.
For instance, if a game shows artifacts but a video player does not, it may be an issue with the game itself or its compatibility with your GPU.
Using Diagnostic Tools
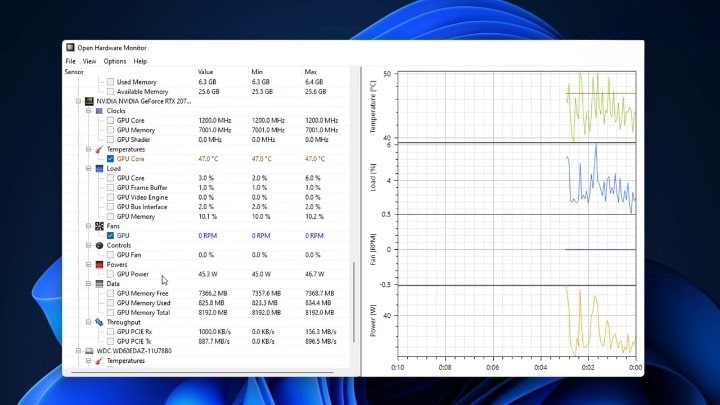
Leverage diagnostic tools to gain insights into your component’s performance. Software like GPU-Z or MSI Afterburner can provide real-time statistics about your GPU’s temperature, clock speed, and other metrics.
Observing these parameters during artifacting can provide clues about overheating or other issues affecting the graphic card.
Simple Fixes to Try First
Sometimes, resolving GPU artifacting doesn’t require intense technical know-how. A few simple fixes might resolve the issue.
Restarting the Computer
It might sound overly simplistic, but sometimes, all it takes is a reboot. Temporary software glitches or minor system hiccups can cause artifacting, and a restart can clear these out.
If the artifacting is gone post-reboot but returns later, it might indicate intermittent issues like overheating or specific application-triggered glitches.
Re-seating the GPU
Physically re-seating the GPU can solve certain connection-related problems. Turn off the PC, unplug it, and carefully remove the graphic cardfrom its slot. Then, securely place it back.
Sometimes, the graphic card might not be correctly seated or dust could be affecting the connection, leading to artifacting. Ensuring a secure and clean connection might resolve the issue.
Addressing Overheating Concerns
Overheating is a common culprit behind GPU artifacting. Ensuring optimal thermal conditions for your graphic cardcan significantly reduce the occurrence of artifacts.
Improving Case Ventilation
A well-ventilated case ensures efficient heat dissipation, maintaining a cooler environment for all components, including the graphic card. Invest in quality case fans that circulate air efficiently throughout the case.
Rearrange internal components, if possible, to minimize obstructions and facilitate smoother airflow.
Cleaning the Graphic Card and Case
Dust accumulation can insulate components, leading to increased temperatures and potential artifacting. Regularly clean the card’s fans and heatsinks using compressed air, ensuring they’re free from dust and debris.
Keeping the case’s interior clean, especially the intake and exhaust areas, will also help maintain optimal airflow and cooling.
Software and Driver Solutions
Sometimes, GPU artifacting stems from software or driver issues rather than hardware. Addressing these can offer a swift resolution.
Updating or Rolling Back Drivers
Drivers act as the bridge between the OS and the hardware. Ensuring they’re up-to-date or reverting to a stable version can fix artifacting. Always download drivers directly from the manufacturer’s official website.
If artifacting started after a recent update, consider rolling back to a previous driver version known for stability.
Adjust the Settings
Overclocking or certain factory settings might be too aggressive for your specific graphic card, causing artifacts. Using software like MSI Afterburner, reduce the clock speeds slightly and observe if the artifacting diminishes.
Ensure that the power supply to the GPU is adequate. If the graphic card isn’t receiving sufficient power, it can result in artifacting.
Evaluating Hardware Integrity
If software solutions don’t resolve the issue, it’s time to inspect the hardware’s integrity.
Checking the Component on Another PC
Isolating the graphic card can help determine if it’s the root cause of the artifacting. If possible, insert the card into another system. If artifacting persists, it’s likely an issue with the GPU itself. Conversely, if the card works flawlessly on another system, the problem might lie elsewhere in the original PC setup.
Inspecting for Physical Damage
A close inspection can sometimes reveal physical anomalies. Check the GPU for any visible signs of damage, like burnt areas, damaged capacitors, or other irregularities. If you discover physical damage, it’s a strong indicator that it needs replacement.
Preventative Measures
Forewarned is forearmed. Adopting proactive measures can prevent GPU artifacting issues before they arise, ensuring a smoother user experience.
Monitor GPU Temperatures Regularly
Being vigilant about your hardware’s temperature can prevent overheating and its associated complications. Utilize monitoring software like HWMonitor or GPU-Z to keep an eye on the temperature during regular use and intensive tasks.
A good practice is to establish a baseline of average temperatures during various activities, which helps identify deviations and potential issues early on.
Regular Maintenance
Just like any piece of machinery, regular maintenance goes a long way in ensuring optimal operation and longevity. Establish a routine to clean your PC’s internals, ensuring dust doesn’t accumulate, which can hamper performance and cooling.
Periodically check for software updates, including BIOS/UEFI updates, which might contain optimizations for hardware compatibility and performance.
When Should You Consult Professionals

While many issues can be resolved with DIY solutions, some situations demand expert attention.
Persistent Artifacting
If, after trying various solutions, the artifacting persists, it might be time to consult an expert. A professional might identify less apparent issues causing the artifacting or recommend hardware replacements if necessary.
Often, repair shops have diagnostic tools and resources not readily available to the average consumer, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis.
Potential Warranty Claims
If your GPU is still under warranty, it’s wise to consider making a claim. Before trying extensive DIY solutions, especially those that might void the warranty, reach out to the manufacturer or seller.
Often, recognized defects or common issues might be addressed by the manufacturer directly, saving time and effort.
The Longevity
Every piece of hardware has a lifespan, and understanding this can help manage expectations and plan for replacements.
Average Lifespan
While this piece of hardware can last for years, various factors influence their longevity. On average, a graphic card might last anywhere from 4 to 6 years under regular use. However, intense activities like prolonged gaming or cryptocurrency mining can reduce this lifespan.
Physical factors, such as manufacturing quality, ventilation, and regular maintenance, also play a role in how long a graphic card serves without issues.
Planning for Upgrades
Keeping abreast of technological advancements ensures you’re not left behind and can enhance your computing experience. Even if your graphic card doesn’t exhibit issues like artifacting, advancements in technology might render older GPUs obsolete for newer applications and games.
Setting aside a budget and periodically evaluating potential upgrades can ensure uninterrupted performance and access to the latest graphical features.
FAQs
Is artifacting always a sign of GPU damage?
Not always. While artifacting can indicate a potential GPU issue, it can also be a result of software discrepancies or other non-hardware-related concerns.
How can I determine if the issue is with my GPU or another component?
One method is to try the GPU in another system. If the artifacting persists, it’s likely the graphic card. If not, the original system might have another component causing the issue.
Do I need to replace my GPU if I see artifacts?
Not immediately. First, try various troubleshooting steps, such as updating drivers or reducing overheating. If all methods fail, consider consulting a professional before deciding on a replacement.
Is there any software to monitor and detect GPU issues before artifacting becomes a major problem?
Yes, tools like HWMonitor, GPU-Z, or MSI Afterburner can help monitor a graphic card’s health and performance, potentially identifying issues before they become severe.
Epilogue
GPU artifacting can be daunting, especially if you rely on your computer for critical tasks or leisure activities. However, with a systematic approach, understanding, and a bit of troubleshooting prowess, most artifacting issues can be addressed efficiently.
Remember, technology is ever-evolving, and staying updated, both in terms of knowledge and hardware, ensures you always enjoy the best visual experience possible.